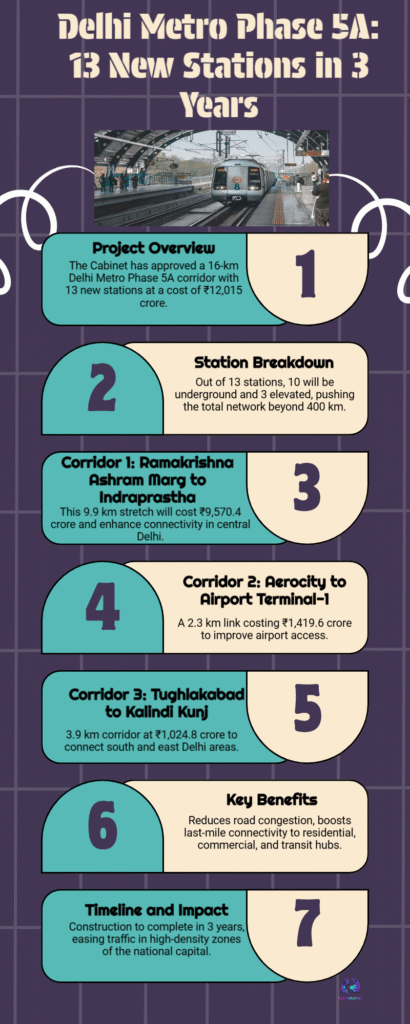
The Delhi Cabinet has approved a major metro expansion plan with 13 new stations over the next three years, strengthening connectivity, easing congestion, and reshaping daily commutes in the capital.
A Significant Push for Public Transport in the Capital
The approval of a fresh metro expansion by the Delhi Cabinet marks a decisive step in the capital’s long-term urban transport planning. With 13 new stations slated to come up over the next three years, the decision reinforces the metro’s role as the backbone of Delhi’s daily mobility. As population density increases and road congestion intensifies, expanding rail-based transit remains central to sustaining the city’s movement.
This expansion is not merely an addition of stations but a recalibration of how the city anticipates growth, distributes access, and integrates transport with evolving urban patterns.
The Scale and Scope of the Expansion
Strategic Addition of New Stations
The plan envisions 13 strategically located stations designed to plug existing connectivity gaps and extend metro access to areas witnessing rapid residential and commercial development. Such targeted expansion helps balance load across the network while drawing more commuters away from private vehicles.
A Defined Three-Year Timeline
Setting a three-year horizon underscores an intent to maintain execution discipline. Metro projects often face delays due to land acquisition, coordination challenges, and logistical complexity. A defined timeframe signals administrative alignment and priority placement within the city’s infrastructure agenda.
Strengthening Connectivity Across Delhi
Linking Emerging Urban Clusters
As Delhi expands outward and densifies inward, mobility needs are shifting. New stations are expected to improve access to peripheral neighborhoods and emerging hubs, reducing dependence on long road journeys and fragmented transport options.
Seamless Integration With Existing Lines
Rather than operating in isolation, the new stations are planned as extensions or connectors within the existing network. This integration ensures continuity of travel, smoother interchanges, and optimal utilization of the metro’s current capacity.
Impact on Daily Commuters
Reduced Travel Time and Congestion
Each additional station has a cumulative effect on reducing surface traffic. By offering closer access points to metro corridors, commuters can shorten first- and last-mile journeys, easing pressure on arterial roads.
Improved Reliability of Commutes
Metro expansion tends to stabilize travel patterns by absorbing peak-hour demand. Over time, this improves punctuality and predictability for millions who rely on public transport for work, education, and essential services.
Urban and Economic Implications
Transit-Oriented Development Momentum
Metro stations often act as anchors for localized development. Commercial activity, housing projects, and public amenities tend to cluster around them, reshaping neighborhoods and redistributing economic activity more evenly across the city.
Employment and Ancillary Growth
Construction, systems integration, and subsequent operations generate direct and indirect employment. Beyond that, improved connectivity supports workforce mobility, enabling businesses to draw talent from a wider catchment area.
Governance and Infrastructure Planning
Coordinated Policy Execution
Large-scale metro expansion requires coordination between multiple agencies—urban development bodies, transport authorities, and municipal administrations. Cabinet-level approval reflects consensus across governance layers, reducing procedural friction.
Long-Term Sustainability Focus
Rail-based transit remains one of the most energy-efficient urban transport modes. Expanding the metro network aligns with broader sustainability goals by curbing vehicular emissions and promoting shared mobility.
Looking Ahead: A Gradual Transformation
The approval of 13 new metro stations is not a sudden overhaul but a measured extension of a system that has steadily reshaped Delhi over the years. As construction progresses and stations become operational, their real impact will unfold gradually—through altered commute habits, evolving neighborhoods, and a city that moves more efficiently.
This expansion reinforces the metro’s status not just as a transport utility, but as a structural element of Delhi’s urban future, shaping how the capital grows, connects, and functions in the years ahead.