India’s GST collections rose 6.1% in December 2025, reflecting steady compliance but visible revenue moderation following recent rate cuts.
GST Revenue Performance in December 2025
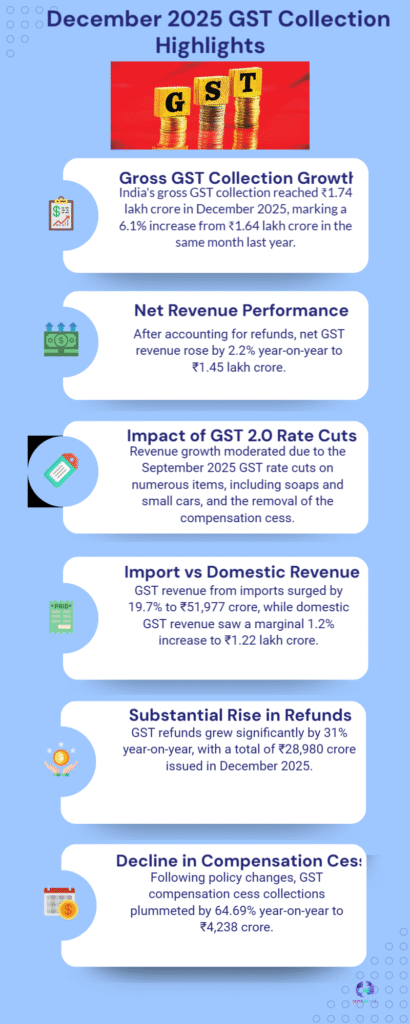
India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections recorded a year-on-year growth of 6.1% in December 2025, marking a phase of moderated expansion after months of stronger momentum. The figures point to a revenue system that remains stable and broad-based, even as recent tax rate adjustments begin to influence the topline.
The December outcome reflects a balance between sustained economic activity and structural policy changes. While consumption levels remained resilient across several sectors, the pace of revenue growth indicates that the cushioning effect of compliance improvements is now sharing space with the arithmetic impact of rate rationalisation.
Understanding the Rate Cut Effect on GST Collections
Policy Intent Behind Rate Rationalisation
GST rate cuts were introduced with the objective of easing the tax burden on select goods and services, supporting demand, and improving affordability. These changes were designed as medium-term economic support measures rather than immediate revenue drivers.
As a result, the December numbers illustrate the first clear signals of how lower rates translate into softer headline growth, even when transaction volumes hold steady.
Volume Versus Value Dynamics
A notable feature of the December data is the divergence between transaction volume and revenue value. While the number of invoices and taxable transactions continued to show healthy movement, the effective tax realised per transaction moderated due to reduced rates in specific slabs.
This shift highlights a structural transition where GST collections are increasingly dependent on economic scale rather than rate intensity.
Compliance and Formalisation Trends Remain Supportive
Stable Tax Base Expansion
Despite slower growth, GST collections continue to benefit from a wider and more formalised tax base. Ongoing digital monitoring, e-invoicing adoption, and tighter return matching have reduced leakages and strengthened reporting discipline.
These factors have prevented sharper deceleration and ensured that collections remain on a stable growth path.
Seasonal and Calendar Influences
December typically reflects mixed seasonal trends, with certain industries experiencing year-end slowdowns while others benefit from festive and consumption-driven demand. The 6.1% growth rate aligns with these cyclical patterns, suggesting no abrupt stress in the underlying tax ecosystem.
What the December Numbers Signal for Fiscal Planning
Revenue Normalisation Phase
The latest GST figures indicate a phase of revenue normalisation rather than contraction. After periods of double-digit growth, moderation was anticipated as policy measures shifted focus from revenue maximisation to economic support.
For fiscal planners, this trend underscores the importance of realistic revenue projections that factor in both policy intent and macroeconomic conditions.
Buffer Through Direct and Indirect Tax Balance
While GST growth has eased, the broader fiscal framework benefits from diversification across direct and indirect taxes. This balance allows the exchequer to absorb short-term moderation in one stream without destabilising overall revenue health.
Outlook for GST Collections in the Coming Months
The December 2025 performance sets the tone for a more measured GST growth trajectory in the near term. As rate cuts continue to work through the system, future collections are likely to mirror economic expansion rather than outperform it.
Sustained compliance gains, combined with gradual consumption recovery, will remain critical in maintaining stability. The focus is shifting from exceptional growth to predictable, policy-aligned revenue outcomes that support long-term fiscal sustainability.
In this context, December’s 6.1% rise serves as a marker of transition—where GST moves deeper into maturity, shaped as much by strategic policy choices as by market-driven activity.