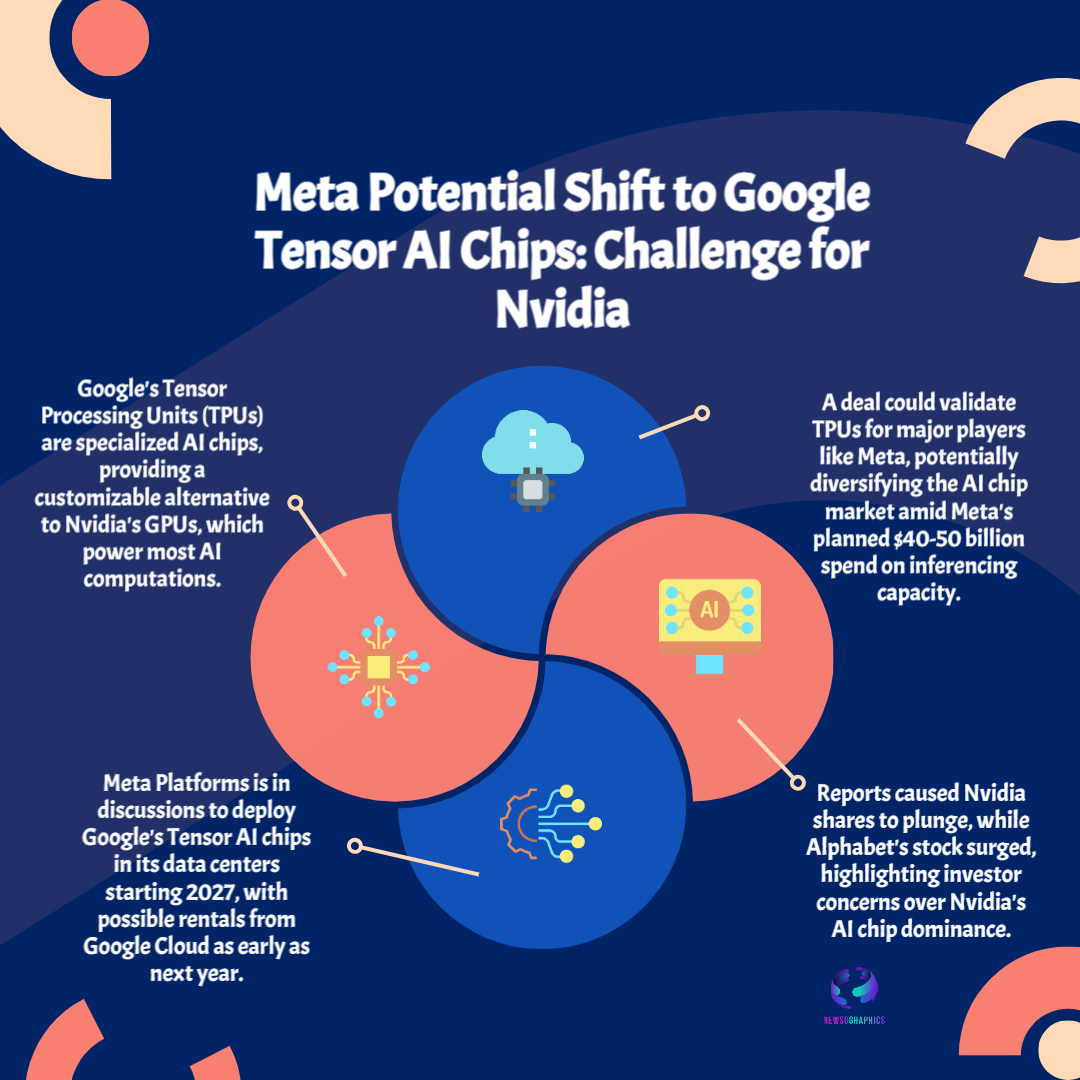
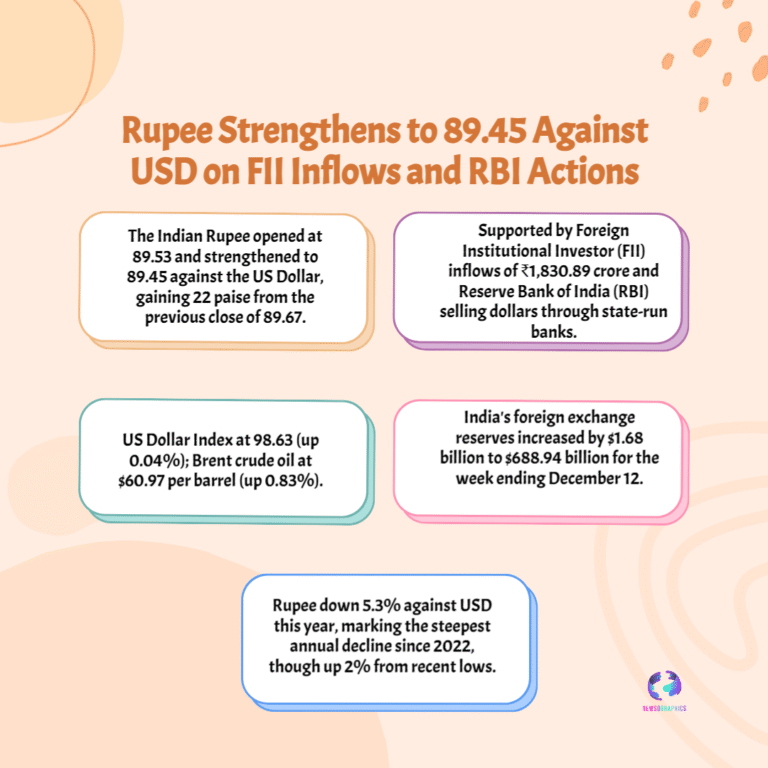
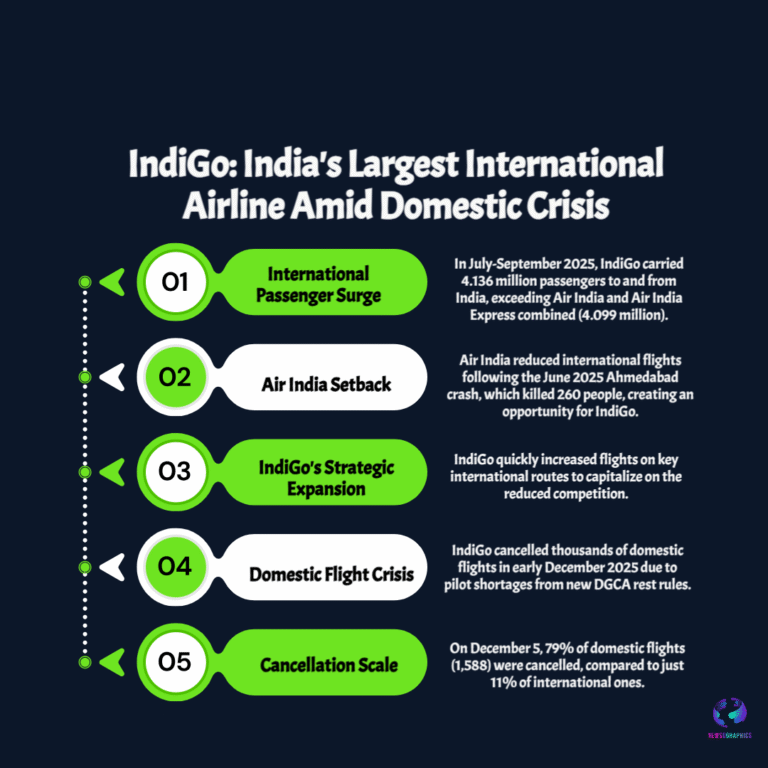
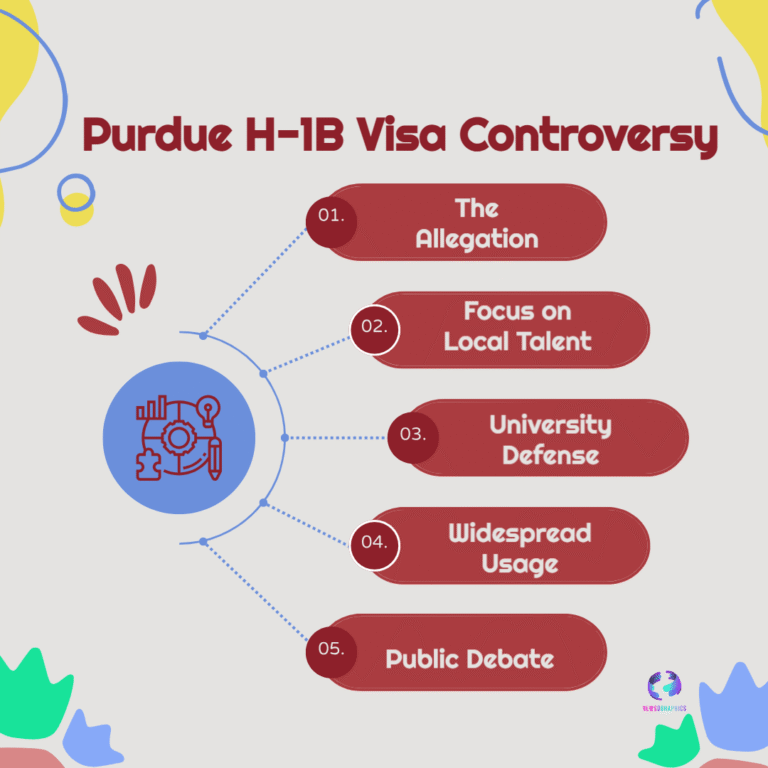
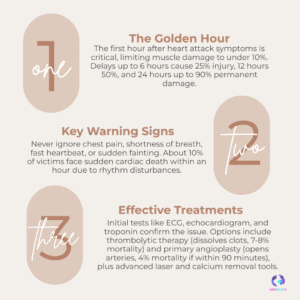
Meta Platforms considers spending billions on Google Tensor AI chips (TPUs) to power its data centers. This strategic shift away from Nvidia’s GPUs signals a huge turning point in the AI silicon market competition.
Meta Taps Google Tensor TPUs
The race to build the next generation of artificial intelligence is no longer just about software algorithms; it is fundamentally about the underlying silicon that powers them. A massive, multi-billion-dollar market shift is currently underway, dramatically underlined by the recent reports that Meta Platforms Inc. is in serious discussions to deploy Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) in its vast global data center infrastructure. This move is not merely a supply-chain adjustment; it represents a direct and credible threat to Nvidia’s GPU market dominance, causing a fresh wave of concern across the entire technology sector.
For the last decade, Nvidia’s Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), originally designed for high-end gaming and graphics rendering, became the accidental, yet indispensable, AI compute engine. Their parallel processing architecture proved perfectly suited for the intense, massive calculations required to train large language models (LLMs). However, this near-monopoly created significant challenges for hyperscalers like Meta, including extremely high costs, long lead times, and an unacceptable over-reliance on a single vendor.